Kano State is implementing a compulsory basic and post-basic education law for primary and secondary students.
In addition, its education sector accounts for approximately 30 percent of the state's annual budget, coupled with the recent declaration of a state of emergency. Yet, weak policy implementation, unenforced relevant laws, and inadequate resources are causing children to roam the streets for alms or hawking at school time. This trend took on a new dimension recently as girls among the children are engaging in unsolicited cleaning of moving vehicles in traffic to survive. However, to address these issues, Kolawole Omoniyi reports that advocates call for an effective Education Sector Plan (ESP) in the state.
At every strategic junction in the Kano metropolis, school-age boys and girls are involved in street begging and hawking during schooltime to fend for themselves and their parents.
The children, some residing in Kano City and others from the outskirts of Local Government Areas (LGAs), travel in and outside the city daily using commercial buses and tricycles.
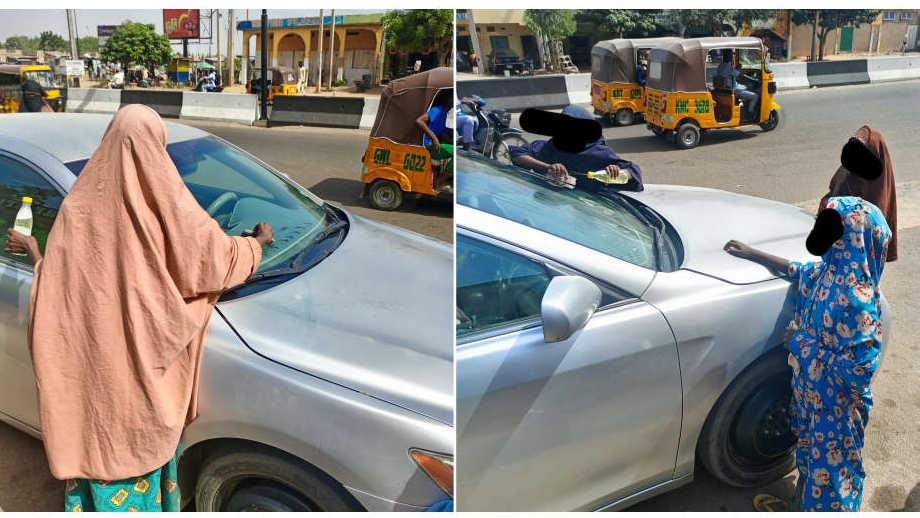
Recently, girls among them have taken on a new dimension by unsolicitedly cleaning cars' windshields to earn money from motorists.
This contravenes the Kano State free and compulsory universal basic and secondary education law 2020, that “the Kano State government would sponsor all children from primary to secondary school.”
Eleven-year-old Ibrahim Fati is among the hundreds of children on Kano streets at school time. She left school because her widowed mother could not afford her learning materials.
Sighted by this reporter along BUK road at Kofar Famfo around 9 a.m. on Wednesday, 20 November, Fati hurriedly left a motorist who resisted her unwelcome gesture to clean his car.
Flanked by her cleaning tools (dusters and a bottle filled with water), Fati quickly moved to the next car in traffic whose driver appeared friendlier. She immediately began her routine cleaning.
“Sai Oga” (the boss)!” Fati persuasively hailed the driver after she partly cleaned the car. The teen was amazed to see the driver alight from the car to engage her instead of giving her the usual token.
“I left school because my mother could not afford to pay for my learning materials,” Fati responded soberly when asked why she was roaming the street during school hours.
Parents Monitor from Vantage Position, Wait for Alms Remittance
“I like to go to school, but there is no money to feed; even two of my siblings are also on this road begging, and our mother is under that kiosk (pointing) to collect the money for feeding,” she explained.
Fati's revelation led to a conversation with her mother, Ibrahim Hadiza, who blames poverty for her actions and believes people have low empathy for adults begging on the streets, unlike children.
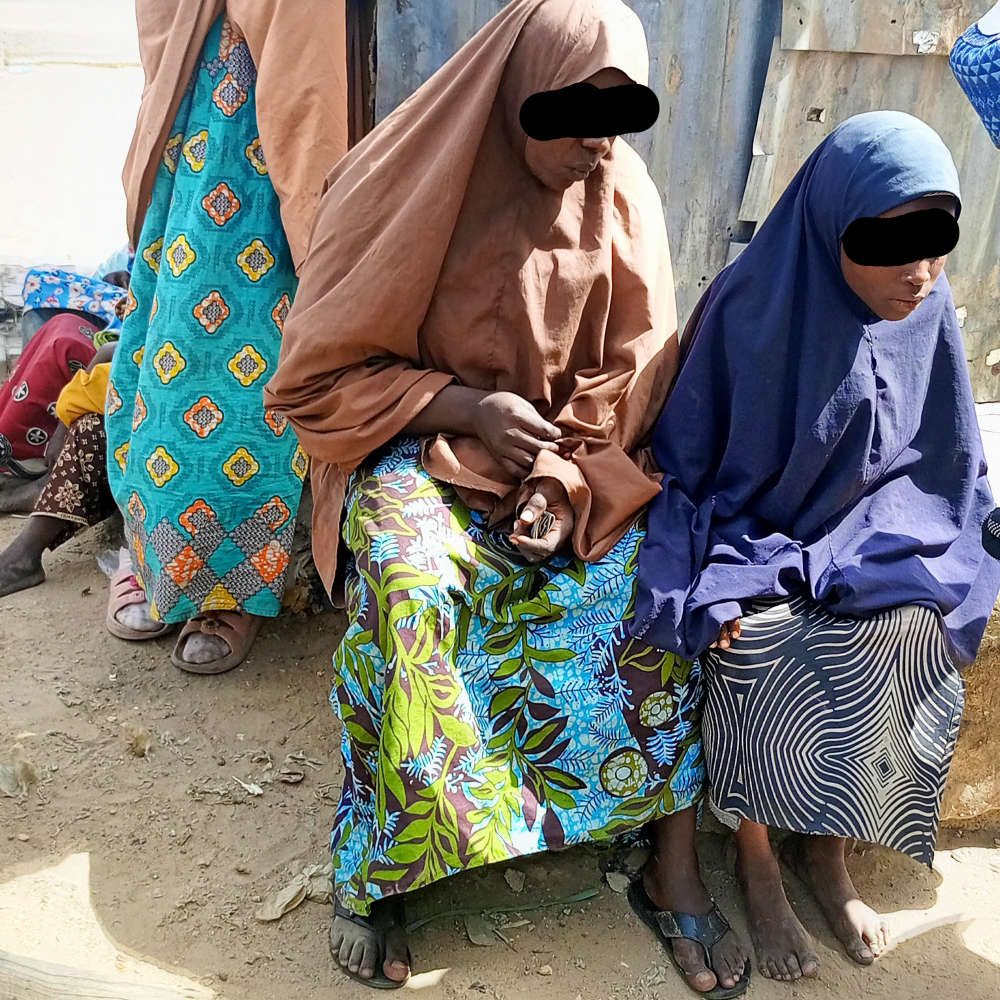

Fati and her mother
“I lost my husband two years ago, and nobody is there for us, which is why we are doing this,” she said.
While the chat with Hadiza lasted, Fati’s two siblings between ages 7 and 9 kept interjecting the conversations at about ten-minute intervals to remit the money they got from motorists.
This trend also takes place at Kofar Kabuga junction along Gwazo Road. But parents and their children at this location resisted several attempts to speak to them. They signaled themselves and vanished into the distance.
Schoolgirls Turn Kano Main Roads to Mini-Markets
Similarly, places like Zoo Road by Court Road and Panshekara Junction in Kumbotso LGA have turned into a mini-market for school-age girls.
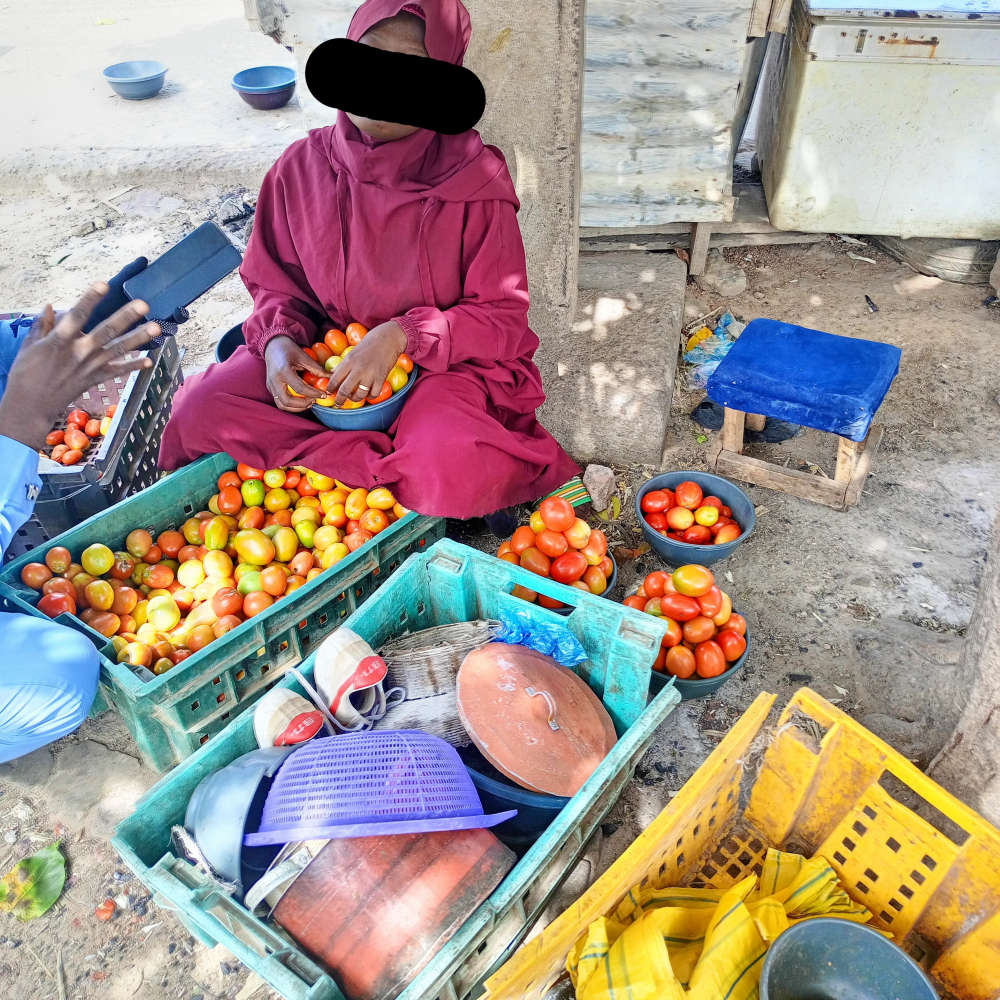
Some of them come from Kura LGA, about 30 kilometers away, to sell perishable goods during school hours.
“We are about 30 in number, coming from Karfi village daily. We used to hire about six tricycles from Kura to come and sell tomatoes here (Zoo Road) and return home in the evening,” Khadija Jubril said.
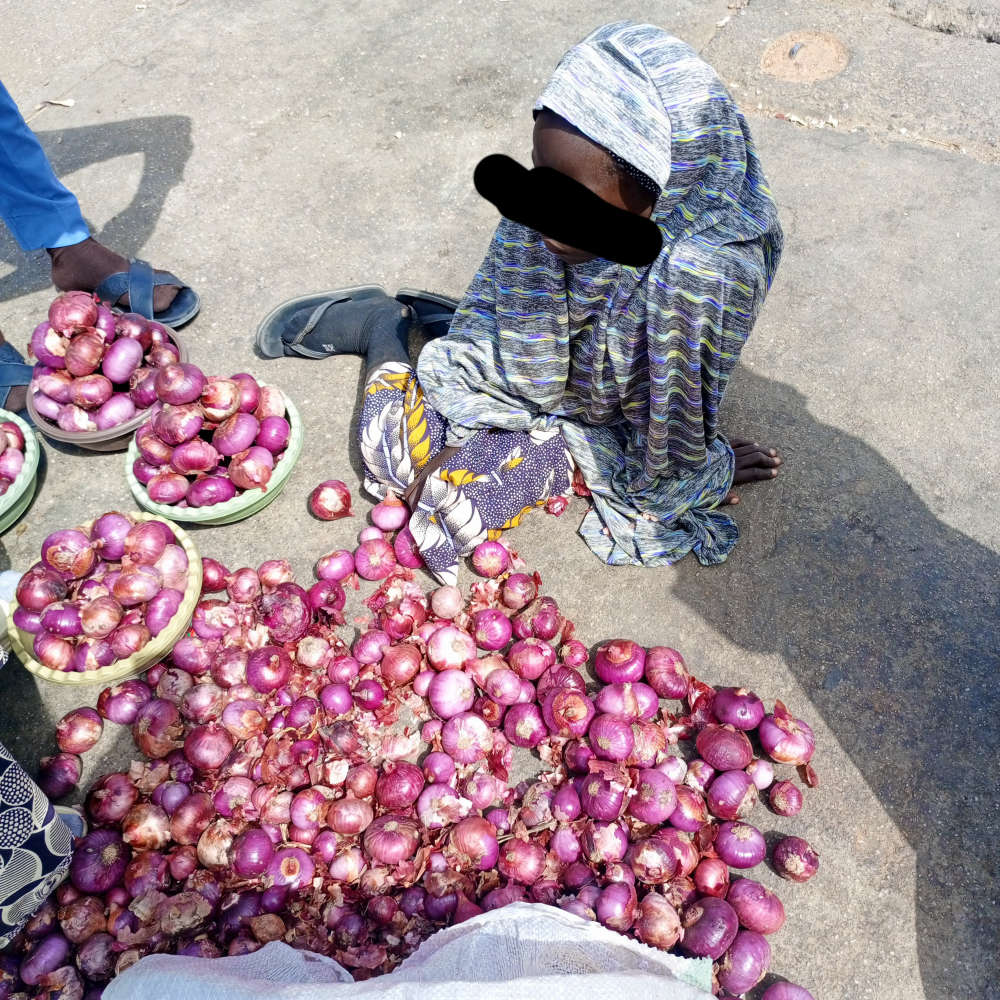

Khadija Jubril
Khadija, 10, explained that she dropped out of Galinja Primary School in Kura LGA, and she has since been selling perishable goods for her parents.
Unlike Khadija, eighteen-year-old Auta Haruna, from the same village, never attended a formal school. She has been saving money from her daily sales to buy clothing materials for her forthcoming wedding next month.
“I’m doing this (hawking) to buy clothes and other materials for my wedding. I’m sure my hustling will end very soon when my husband eventually marries me and starts taking care of me," she said.

Auta Haruna
The situation is not different along Panshekara Road. The area is experiencing a daily influx of tween girls from rural areas to the pyramid city for school-time petty trading adventures.
These communities include 'Dan Baure, Tashar 'Kaba, Tashar Ice, and Kwanar Zuwo, all situated in the Madobi local government area of Kano State.
Sadiya Yahaya, 16, comes from 'Dan Baure village in Madobi to sell boiled cassava daily at Sabon Titi, in Kano City.
“I used to collect raw cassava from some vendors; my mother does the cooking very early, while I transport it to the city for sale. I dropped out of JSS 1 class years back,” she narrated.
Her story is similar to that of Saliha Zailani, 14, who has been selling peanuts for three years from morning till evening in the Sabon Titi area.
“Most of my friends and I from Madobi LGA usually assemble here (Sabon Titi) daily from morning to evening to sell some edible items such as boiled cassava, groundnuts, peanuts, Kuli-Kuli, and cooking oil. We remit the monies to our parents in the evening."
However, these girls are among the significant number of out-of-school children in Kano. Their revelations showcase how poverty and other socio-economic factors are driving out-of-school children in the state.
In October 2023, UNICEF reported that Kano State has at least 989,234 out-of-school children. This is a significant increase from 2016, when only 81,919 children were out of school.
Kano Compulsory Educatiuon Law Remains Toothless
Section 4 of the Kano State Free and Compulsory Universal Basic and Secondary Education Law 2020 stipulates that “it shall be the right of every child in the state to be provided with free and compulsory universal basic education up to secondary school level by the state.”
The law prohibits the collection of fees or money for writing materials in public schools to support individuals like Ibrahim Fati, who is in poverty.
Section 9 (1) of the law states, “It shall not be lawful for any person to collect any fee, in public schools, from any pupil or child in respect of the provision of education as provided in this law.”
Also, sub-section (2) states further, “Any person who obtains any fee contrary to the provisions of this law commits an offence and is liable on conviction to a fine of not less than N20,000 or imprisonment for one month and forfeiture of the fee received in contravention of this law.”
Section 10 of the law also imposes sanctions on defaulting parents: “A parent who fails or neglects to allow his child to enjoy the provision of section 4 of this law commits an offense and is liable on conviction: (a) as a first offender, to verbal reprimand; (b) on subsequent offense, each to a fine of N5,000.00 or one-month imprisonment.”
The Kano State Hisbah Board is responsible for enforcement of the law against street begging and hawking, but its deputy commandant, Mujahideen Aminuddeen, says they are applying a human face to the law.
“Kano is a multi-dimensional state. We have different classes of individuals; sometimes we have to go strictly, and sometimes we have to apply politics because you cannot impose a law while people of Kano State are suffering from poverty; therefore, individuals that are hawking, we will catch them, rehabilitate them, and reintegrate them,” he said.
In February 2024, the state commissioner for education, Umar Doguwa, threatened to enforce this law by taking decisive action against parents whose children were found roaming streets during school hours, yet the children are flooding Kano streets unhindered during school time.
Beyond Enforcement
However, beyond the mere threat of enforcing the free and compulsory basic and post-basic education law in Kano, there are unaddressed fundamental issues hindering the effectiveness of learning in the state.
They include, but are not limited to, poor infrastructure, shortage of teachers, poverty and population spark, insufficient release of funds allocated for capital projects, misplaced priority, and lack of political will.
For instance, UNESCO recommends 35:1 as the ratio of students to teachers, but the Kano ratio is 131:1. Also, according to the Kano Annual School Census 2023, out of the 42,516 classrooms of primary schools, only 22 percent were habitable, as nearly four of every five of them were marked by dilapidation and disrepair.
Also, at the secondary school level, only less than 30 percent of the classrooms were habitable.
Besides the dilapidation, the state has 7,048 primary schools, 1,148 junior secondary schools, and just 813 senior secondary schools, according to the Annual School Census (2021).
This retrogressive number of schools from primary to senior secondary is contributing to the out-of-school children and a decline in retention and completion rates.
State of Emergency
Barely a year into his tenure, Kano State Governor Abba Kabir Yusuf declared a state of emergency in the education sector on June 8, 2024, to address the decay and neglect that had plagued the sector for years.
The state of emergency declaration seemingly reflects in the proposed 2025 appropriation bill recently sent to the state house of assembly, where Governor Yusuf allocated 31% of the state annual budget to education.
However, while there was a lot of publicity about the huge budget allocations, even beyond UNESCO’s 26% recommendation, the percentage of funds being eventually released and areas of priorities remain unclear.
The state government claims at several fora that the state of emergency declaration on education is yielding results, citing ongoing construction of blocks of four classrooms each in primary schools, provision of furniture, and instructional materials, and deployment of additional teaching staff.
The education commissioner added the distribution of one million school uniforms and 73,800 three-seat desks to schools statewide, the provision of school buses to enhance girl child education, and foreign scholarships for about 1,001 postgraduate students.

Governor Yusuf with Kano State Foreign Scholarship Students at Sharjah University, India
Many Initiatives
Meanwhile, Kano is implementing several staggered initiatives and policies to enhance its education sector. They include the 2024 Education Sector Action Plan (AoP) in Kano, the Kano State Development Plan (KSDP), the Girls’ Education and Skills Program, Conditional Cash Transfer Schemes, and the Adolescent Girls Initiative for Learning and Empowerment (AGILE) World Bank project.
Others are the proposed laws and policies currently before the state executive council: Kano Education Law, 2024; Kano Teacher Development Policy; Kano Non-State Actor Policy; Kano State Early Child Care & Development (ECCD); and Kano State Girl-Child Education Policy.
However, despite these initiatives and policies, Kano schools still face challenges such as poor access, infrastructure, high dropout rates, teacher shortages, and lack of basic materials like desks, chairs, toilets, and instructional materials.
So, What is Missing?
It appears that the lack of a functioning Education Sector Plan (ESP) in Kano is causing a lack of coordination of the initiatives by mainstreaming their operations and ensuring effective monitoring and evaluation.
According to UNESCO, an education sector plan is a national policy instrument, involving government responsibility, providing a long-term vision, and strategies for the education system. By default, this is also applicable to state governments.
Regrettably, the 2009 Education Sector Plan in Kano, which was intended to last for ten years, expired in 2018. Consequently, most of the subsequent initiatives in the sector lack SMART goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound.